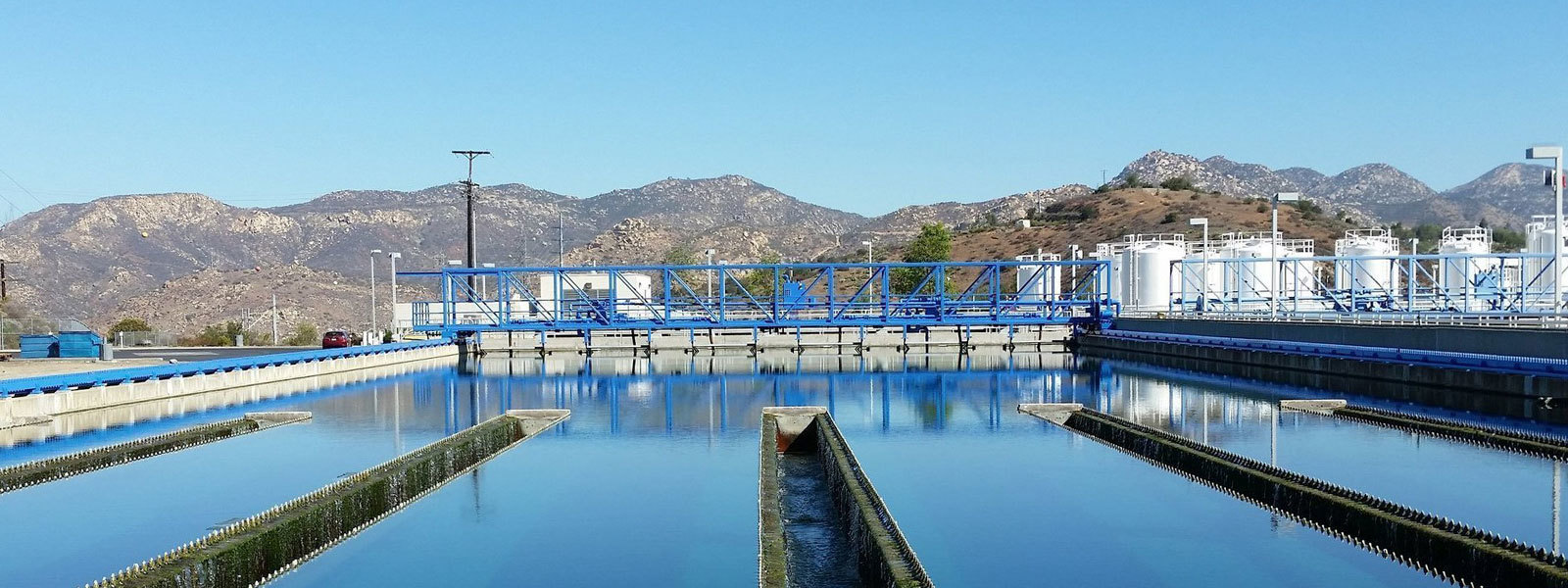
Polyacrylamide using in Municipal Wastewater Treatment
Release time:
Apr 02,2024
Polyacrylamide use in Municipal Wastewater Treatment

Introduction:
Municipal wastewater treatment is a critical process to safeguard public health and the environment by removing contaminants from wastewater before discharge into natural water bodies. Polyacrylamide (PAM) has emerged as a valuable chemical in this domain due to its excellent flocculation properties, which facilitate the removal of suspended solids and pollutants from wastewater. This article provides an overview of the application of polyacrylamide in municipal wastewater treatment processes.
Flocculation and Coagulation:
Polyacrylamide is commonly used as a flocculant in municipal wastewater treatment plants to enhance the sedimentation and filtration processes. When added to wastewater, PAM molecules form large, sticky flocs by attracting and binding suspended particles together. These flocs settle more rapidly, allowing for efficient removal of solids and impurities from the water. Moreover, polyacrylamide can aid in the coagulation process by destabilizing colloidal particles and promoting their aggregation, further improving the efficiency of wastewater treatment.
Reduction of Turbidity:
Turbidity, caused by suspended particles in wastewater, can impair water quality and interfere with disinfection processes. Polyacrylamide aids in reducing turbidity by effectively aggregating and settling suspended solids, thereby clarifying the water. This is particularly crucial in municipal wastewater treatment, where clear effluent is essential before discharge into receiving water bodies or reuse.
Enhanced Sludge Dewatering:
In addition to its role in primary wastewater treatment, polyacrylamide is also utilized in sludge dewatering processes. By promoting the formation of larger and denser flocs, PAM facilitates the separation of water from sludge, leading to higher dewatering efficiency and reduced disposal costs. The use of polyacrylamide in sludge dewatering can significantly improve the overall performance and sustainability of municipal wastewater treatment plants.
Compatibility and Safety:
Polyacrylamide is known for its compatibility with other chemicals commonly used in wastewater treatment, such as coagulants and disinfectants. It can be easily integrated into existing treatment processes without causing adverse effects or compromising system performance. Moreover, modern formulations of polyacrylamide are designed to meet stringent environmental and safety standards, ensuring its safe and sustainable application in municipal wastewater treatment.
Conclusion:
Polyacrylamide plays a vital role in municipal wastewater treatment by improving flocculation, reducing turbidity, and enhancing sludge dewatering processes. Its versatility, compatibility, and effectiveness make it a valuable chemical additive for achieving efficient and environmentally sustainable wastewater treatment outcomes. Continued research and innovation in the application of polyacrylamide hold promise for further advancements in municipal wastewater treatment technology.
Related News
xinqi polymer New Product Catalog
Aug 04,2025
Jul 19,2025
water and wastewater treatment chemicals
Jul 04,2025
cationic polymer flocculant suppliers
Jul 01,2025